
Anthony Ottombrino
356 Tysens Ln
Staten Island NY 10306-2843
Staten Island NY 10306-2843
Inspector: Anthony Ottombrino

Summary
| Client(s): | Mariela fiqueroa & Leorel Jimenez |
| Property address: | 55 Lynhurst Ave Staten Island NY 10305-1808 |
| Inspection date: | Saturday, July 2, 2022 |
This report published on Sunday, July 3, 2022 7:05:43 PM EDT
This report is the exclusive property of this inspection company and the client(s) listed in the report title. Use of this report by any unauthorized persons is prohibited.
| Safety | Poses a safety hazard | |
| Major Defect | Correction likely involves a significant expense | |
| Repair/Replace | Recommend repairing or replacing | |
| Repair/Maintain | Recommend repair and/or maintenance | |
| Minor Defect | Correction likely involves only a minor expense | |
| Maintain | Recommend ongoing maintenance | |
| Evaluate | Recommend evaluation by a specialist | |
| Monitor | Recommend monitoring in the future | |
| Comment | For your information |
General Information
1) 
 Structures built prior to the mid 1980s may contain lead and/or asbestos. Lead is commonly found in paint and in some plumbing components. The EPA does not recognize newer coats of paint as encapsulating older coats of lead-based paint. Asbestos is commonly found in various building materials such as insulation, siding, and/or floor and ceiling tiles. Laws were passed in 1978 to prohibit usage of lead and asbestos, but stocks of materials containing these substances remained in use for a number of years thereafter. Both lead and asbestos are known health hazards. Evaluating for the presence of lead and/or asbestos is beyond the scope of this inspection. Any mention of these materials in this report is made as a courtesy only, and meant to refer the client to a specialist. Consult with specialists as necessary, such as industrial hygienists, professional labs and/or abatement specialists for this type of evaluation. For information on lead, asbestos and other hazardous materials in homes, visit:
Structures built prior to the mid 1980s may contain lead and/or asbestos. Lead is commonly found in paint and in some plumbing components. The EPA does not recognize newer coats of paint as encapsulating older coats of lead-based paint. Asbestos is commonly found in various building materials such as insulation, siding, and/or floor and ceiling tiles. Laws were passed in 1978 to prohibit usage of lead and asbestos, but stocks of materials containing these substances remained in use for a number of years thereafter. Both lead and asbestos are known health hazards. Evaluating for the presence of lead and/or asbestos is beyond the scope of this inspection. Any mention of these materials in this report is made as a courtesy only, and meant to refer the client to a specialist. Consult with specialists as necessary, such as industrial hygienists, professional labs and/or abatement specialists for this type of evaluation. For information on lead, asbestos and other hazardous materials in homes, visit:
http://www.reporthost.com/?EPA
http://www.reporthost.com/?CPSC
http://www.reporthost.com/?CDC
http://www.reporthost.com/?EPA
http://www.reporthost.com/?CPSC
http://www.reporthost.com/?CDC
Grounds
3) 
 Handrails at one or more flights of stairs were missing. This is a potential fall hazard. Handrails should be installed at stairs with four or more risers or where stairs are greater than 30 inches high. Recommend that a qualified contractor install handrails where missing and per standard building practices.
Handrails at one or more flights of stairs were missing. This is a potential fall hazard. Handrails should be installed at stairs with four or more risers or where stairs are greater than 30 inches high. Recommend that a qualified contractor install handrails where missing and per standard building practices.
4) 
 Guardrails above retaining walls higher than 30 inches were Loose. This is a safety hazard due to the risk of falling. At a minimum, the client should be aware of this hazard, especially when children are present. Recommend that a qualified contractor install or repair guardrails per standard building practices (e.g. minimum 3 feet high, no gaps wider than 4 inches, not climbable). Dense shrubbery or vegetation may be acceptable as a barrier, but only when mature enough to be effective.
Guardrails above retaining walls higher than 30 inches were Loose. This is a safety hazard due to the risk of falling. At a minimum, the client should be aware of this hazard, especially when children are present. Recommend that a qualified contractor install or repair guardrails per standard building practices (e.g. minimum 3 feet high, no gaps wider than 4 inches, not climbable). Dense shrubbery or vegetation may be acceptable as a barrier, but only when mature enough to be effective.
5) 
 No drain was visible at the bottom of one or more sets of stairs. Water may accumulate at the bottom of the stairs and be a nuisance, or enter the building. Monitor drains in the future during periods of heavy rain. If water is found to accumulate, then recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary to allow for drainage, and to prevent water accumulation. For example, by installing a drain, sump pump or stairwell roof.
No drain was visible at the bottom of one or more sets of stairs. Water may accumulate at the bottom of the stairs and be a nuisance, or enter the building. Monitor drains in the future during periods of heavy rain. If water is found to accumulate, then recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary to allow for drainage, and to prevent water accumulation. For example, by installing a drain, sump pump or stairwell roof.
6)  Masonry steps have settled significantly, or significant cracks or deterioration were found. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair or replace steps as necessary.
Masonry steps have settled significantly, or significant cracks or deterioration were found. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair or replace steps as necessary.
Exterior and Foundation
7) 
 The parging (decorative coating) on one or more foundation walls was damaged or deteriorated. This is not a structural concern, but the client may want this repaired for appearance's sake.
The parging (decorative coating) on one or more foundation walls was damaged or deteriorated. This is not a structural concern, but the client may want this repaired for appearance's sake.
8)  One or more holes or gaps were found in or below the foundation. Vermin may enter the building substructure as a result. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
One or more holes or gaps were found in or below the foundation. Vermin may enter the building substructure as a result. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
9)  Caulk was missing and/or deteriorated in some areas. For example, around windows, around doors and/or at siding-trim junctions. Recommend that a qualified person renew or install caulk as necessary. Where gaps are wider than 1/4 inch, an appropriate material other than caulk should be used. For more information, visit:
Caulk was missing and/or deteriorated in some areas. For example, around windows, around doors and/or at siding-trim junctions. Recommend that a qualified person renew or install caulk as necessary. Where gaps are wider than 1/4 inch, an appropriate material other than caulk should be used. For more information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?CAULK
https://www.reporthost.com/?CAULK
Plumbing / Fuel Systems
11) 
 One or more black steel gas supply pipes had substandard support or were loose. Gas leaks may occur as a result. Black steel gas supply pipes should have approved hangers every 6-8 feet. Hangers should be made from steel to prevent the pipes and hangers from corroding due to contact of dissimilar metals. Recommend that a qualified person install hangers or secure pipes per standard building practices.
One or more black steel gas supply pipes had substandard support or were loose. Gas leaks may occur as a result. Black steel gas supply pipes should have approved hangers every 6-8 feet. Hangers should be made from steel to prevent the pipes and hangers from corroding due to contact of dissimilar metals. Recommend that a qualified person install hangers or secure pipes per standard building practices.
12) 
 Copper water supply pipes were installed. Copper pipes installed prior to the late 1980s may be joined with solder that contains lead, which is a known health hazard especially for children. Laws were passed in 1985 prohibiting the use of lead in solder, but prior to that solder normally contained approximately 50% lead. The client should be aware of this, especially if children will be using this water supply system. Note that the inspector does not test for toxic materials such as lead. The client should consider having a qualified lab test for lead, and if necessary take steps to reduce or remove lead from the water supply. Various solutions include:
Copper water supply pipes were installed. Copper pipes installed prior to the late 1980s may be joined with solder that contains lead, which is a known health hazard especially for children. Laws were passed in 1985 prohibiting the use of lead in solder, but prior to that solder normally contained approximately 50% lead. The client should be aware of this, especially if children will be using this water supply system. Note that the inspector does not test for toxic materials such as lead. The client should consider having a qualified lab test for lead, and if necessary take steps to reduce or remove lead from the water supply. Various solutions include:
https://www.reporthost.com/?LEADDW
https://www.reporthost.com/?LEAD
- Flush water taps or faucets. Do not drink water that has been sitting in the plumbing lines for more than 6 hours
- Install appropriate filters at points of use
- Use only cold water for cooking and drinking, as hot water dissolves lead more quickly than cold water
- Use bottled or distilled water
- Treat well water to make it less corrosive
- Have a qualified plumber replace supply pipes and/or plumbing components as necessary
https://www.reporthost.com/?LEADDW
https://www.reporthost.com/?LEAD
13) 


 One or more leaks were found in waste pipes or fittings. A qualified plumber should evaluate and repair as necessary.
One or more leaks were found in waste pipes or fittings. A qualified plumber should evaluate and repair as necessary.
Recommend a further sewer scope of the main sewer line due to the age of the building.
Recommend a further sewer scope of the main sewer line due to the age of the building.
14)  Water supply pipes in the crawl space were not insulated. Recommend insulating pipes per standard building practices to prevent them from freezing during cold weather, and for better energy efficiency with hot water supply pipes.
Water supply pipes in the crawl space were not insulated. Recommend insulating pipes per standard building practices to prevent them from freezing during cold weather, and for better energy efficiency with hot water supply pipes.
15)  No hose bibs were found. Recommend that a qualified plumber install one or more hose bibs for convenience, and per standard building practices (e.g. frost-free with anti-siphon device).
No hose bibs were found. Recommend that a qualified plumber install one or more hose bibs for convenience, and per standard building practices (e.g. frost-free with anti-siphon device).
16)  The sump pump is connected to discharge into the main sewer line this is not a legal practice, all connections should be discharged outdoors or into a storm drain. Recommend a qualified contractor repair as per standard building practice.
The sump pump is connected to discharge into the main sewer line this is not a legal practice, all connections should be discharged outdoors or into a storm drain. Recommend a qualified contractor repair as per standard building practice.
17)  One or more plastic PEX water supply pipes had substandard support or were loose. Leaks can occur as a result. PEX supply pipes should have approved hangers every 32-36 inches when run horizontally. Special hangers that allow movement from expansion and that won't damage the soft plastic piping should be used. Recommend that a qualified person install hangers or secure pipes per standard building practices.
One or more plastic PEX water supply pipes had substandard support or were loose. Leaks can occur as a result. PEX supply pipes should have approved hangers every 32-36 inches when run horizontally. Special hangers that allow movement from expansion and that won't damage the soft plastic piping should be used. Recommend that a qualified person install hangers or secure pipes per standard building practices.
18)  One or more ABS or PVC plastic drain pipes had substandard support or were loose. Leaks can occur as a result. Such pipes should have hangers every 4 feet when run horizontally. Recommend that a qualified person install hangers or secure pipes per standard building practices.
One or more ABS or PVC plastic drain pipes had substandard support or were loose. Leaks can occur as a result. Such pipes should have hangers every 4 feet when run horizontally. Recommend that a qualified person install hangers or secure pipes per standard building practices.
19)  One or more waste line clean-out caps were missing, damaged or substandard. Leaks can occur or sewer gases can enter living spaces as a result. Recommend that a qualified plumber replace the cap(s) as necessary.
One or more waste line clean-out caps were missing, damaged or substandard. Leaks can occur or sewer gases can enter living spaces as a result. Recommend that a qualified plumber replace the cap(s) as necessary.
Water Heater
24)  Water heater missing sediment trap.
Water heater missing sediment trap.
sediment traps are designed to catch sediment, in natural gas, before it enters into the water heater or furnace gas valve. Different areas have different contaminants in the gas, and the traps help catch these.
most water heaters do not have sediment traps in them. When new water heaters are installed , it is generally one of the requirements when a permit is obtained and it is recommended by the water heater manufacturer.
sediment traps are designed to catch sediment, in natural gas, before it enters into the water heater or furnace gas valve. Different areas have different contaminants in the gas, and the traps help catch these.
most water heaters do not have sediment traps in them. When new water heaters are installed , it is generally one of the requirements when a permit is obtained and it is recommended by the water heater manufacturer.
Fireplaces, Stoves, Chimneys and Flues
27) 
 No spark screen or rain cap was installed at one or more chimney flue terminations. Spark screens reduce the chance of embers exiting the flue and causing fires. They also prevent wildlife (e.g. birds, rodents, raccoons) from entering flues. Rain caps prevent water from entering flues, mixing with combustion deposits and creating caustic chemicals which can corrode flues. They also prevent damage to masonry from freeze-thaw cycles and prevent metal components (e.g. dampers, metal firebox liners) from rusting. Recommend that a qualified person install rain caps with spark screens per standard building practices where missing.
No spark screen or rain cap was installed at one or more chimney flue terminations. Spark screens reduce the chance of embers exiting the flue and causing fires. They also prevent wildlife (e.g. birds, rodents, raccoons) from entering flues. Rain caps prevent water from entering flues, mixing with combustion deposits and creating caustic chemicals which can corrode flues. They also prevent damage to masonry from freeze-thaw cycles and prevent metal components (e.g. dampers, metal firebox liners) from rusting. Recommend that a qualified person install rain caps with spark screens per standard building practices where missing.
28) 
 One or more gas-fired appliances such as a furnace or water heater used a masonry chimney for venting, and no metal flue liner was visible. Metal liners should be installed to prevent drafting problems from an over-sized flue, to prevent corrosive exhaust gases from damaging the masonry chimney, and to prevent exhaust gases from leaking through gaps or seams in the chimney. This is a potential safety hazard. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair per standard building practices. For example, by installing a metal liner. For more information search for "liner" at:
One or more gas-fired appliances such as a furnace or water heater used a masonry chimney for venting, and no metal flue liner was visible. Metal liners should be installed to prevent drafting problems from an over-sized flue, to prevent corrosive exhaust gases from damaging the masonry chimney, and to prevent exhaust gases from leaking through gaps or seams in the chimney. This is a potential safety hazard. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair per standard building practices. For example, by installing a metal liner. For more information search for "liner" at:
https://www.reporthost.com/?CSIA
https://www.reporthost.com/?CSIA
29)  One or more masonry chimney crowns were cracked. Crowns are meant to keep water off of the chimney structure and prevent damage from freeze-thaw cycles. Chimney crowns are commonly constructed by mounding concrete or mortar on the top chimney surface, however this is substandard. A properly constructed chimney crown should:
One or more masonry chimney crowns were cracked. Crowns are meant to keep water off of the chimney structure and prevent damage from freeze-thaw cycles. Chimney crowns are commonly constructed by mounding concrete or mortar on the top chimney surface, however this is substandard. A properly constructed chimney crown should:
- Be constructed using either precast concrete slabs, cast-in-place steel reinforced concrete, solid stone, or metal
- Be sloped down from the flue a minimum of 3 inches of fall per foot of run
- Extend a minimum of 2 1/2 inches beyond the face of the chimney on all sides
- Not directly contact the flue liner (if installed), with the gap filled with flexible caulk
- Have flashing installed between the bottom of the crown and the top of the brick chimney
Kitchen
30) 
 The dishwasher was . Recommend that a qualified specialist evaluate and repair or replace as necessary.
The dishwasher was . Recommend that a qualified specialist evaluate and repair or replace as necessary.
31) 
 The exhaust fan over the range recirculated the exhaust air back into the kitchen. This may be due to no duct being installed, baffles not being installed, or problems with duct work. This can be a nuisance for odor and grease accumulation. Where a gas-fired range or cook top is installed, carbon monoxide and excessive levels of moisture can accumulate in living spaces. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary so exhaust air is ducted outdoors.
The exhaust fan over the range recirculated the exhaust air back into the kitchen. This may be due to no duct being installed, baffles not being installed, or problems with duct work. This can be a nuisance for odor and grease accumulation. Where a gas-fired range or cook top is installed, carbon monoxide and excessive levels of moisture can accumulate in living spaces. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair as necessary so exhaust air is ducted outdoors.
Bathrooms, Laundry and Sinks
34)  The bathroom with a shower or bathtub at location(s) #B didn't have an exhaust fan installed. Moisture can accumulate and result in mold, bacteria or fungal growth. Even if the bathroom has a window that opens, it may not provide adequate ventilation, especially during cold weather when windows are closed or when wind blows air into the bathroom. Recommend that a qualified contractor install exhaust fans per standard building practices where missing in bathrooms with showers or bathtubs.
The bathroom with a shower or bathtub at location(s) #B didn't have an exhaust fan installed. Moisture can accumulate and result in mold, bacteria or fungal growth. Even if the bathroom has a window that opens, it may not provide adequate ventilation, especially during cold weather when windows are closed or when wind blows air into the bathroom. Recommend that a qualified contractor install exhaust fans per standard building practices where missing in bathrooms with showers or bathtubs.
35)  The laundry room didn't have an exhaust fan installed. Moisture can accumulate and result in mold, bacteria or fungal growth. Recommend that a qualified contractor install an exhaust fan per standard building practices.
The laundry room didn't have an exhaust fan installed. Moisture can accumulate and result in mold, bacteria or fungal growth. Recommend that a qualified contractor install an exhaust fan per standard building practices.
36)  No exhaust duct was installed for the clothes dryer. Clothes dryers produce large amounts of moisture which should not enter structure interiors. Moisture can accumulate and result in mold, bacteria or fungal growth. A rigid or semi-rigid metal exhaust duct should be installed per standard building practices, and by a qualified contractor if necessary. For information, visit:
No exhaust duct was installed for the clothes dryer. Clothes dryers produce large amounts of moisture which should not enter structure interiors. Moisture can accumulate and result in mold, bacteria or fungal growth. A rigid or semi-rigid metal exhaust duct should be installed per standard building practices, and by a qualified contractor if necessary. For information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?DRYER
https://www.reporthost.com/?DRYER
37) 
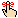 The bathtub at location(s) #B drained slowly. Recommend clearing drain and/or that a qualified plumber repair if necessary.
The bathtub at location(s) #B drained slowly. Recommend clearing drain and/or that a qualified plumber repair if necessary.
38)  Ribbed, flexible drain pipe was used at the sink at location(s) #B. This type of drain pipe accumulates debris more easily than smooth wall pipe and is likely to clog. Recommend that a qualified plumber replace flexible piping with standard plumbing components (smooth wall pipe) to prevent clogged drains.
Ribbed, flexible drain pipe was used at the sink at location(s) #B. This type of drain pipe accumulates debris more easily than smooth wall pipe and is likely to clog. Recommend that a qualified plumber replace flexible piping with standard plumbing components (smooth wall pipe) to prevent clogged drains.
Interior, Doors and Windows
39) 
 Treads for stairs at one or more locations were less than 10 inches deep and pose a fall or trip hazard. Stair treads should be at least 10 inches deep. At a minimum, be aware of this hazard, especially when guests who are not familiar with the stairs are present. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair per standard building practices.
Treads for stairs at one or more locations were less than 10 inches deep and pose a fall or trip hazard. Stair treads should be at least 10 inches deep. At a minimum, be aware of this hazard, especially when guests who are not familiar with the stairs are present. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair per standard building practices.
40)  The glazing compound or caulk that holds glass panes in one or more windows was deteriorated and/or substandard. Air and/or water can leak through windows, and wood window frames are prone to rot. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend that a qualified person replace glazing compound as necessary. For more information, visit:
The glazing compound or caulk that holds glass panes in one or more windows was deteriorated and/or substandard. Air and/or water can leak through windows, and wood window frames are prone to rot. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend that a qualified person replace glazing compound as necessary. For more information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?PUTTY
https://www.reporthost.com/?PUTTY
Roof
42) 
 The roof surface appeared to be near the end of its service life and will likely need replacing in the near future even if repairs are made now. Recommend discussing replacement options with a qualified contractor, and budgeting for a replacement roof surface in the near future. The client may also wish to consider having a qualified contractor attempt to issue a "5 year roof certificate."
The roof surface appeared to be near the end of its service life and will likely need replacing in the near future even if repairs are made now. Recommend discussing replacement options with a qualified contractor, and budgeting for a replacement roof surface in the near future. The client may also wish to consider having a qualified contractor attempt to issue a "5 year roof certificate."
43) 
 Substandard repairs were found at one or more locations on the roof surface. Leaks can occur as a result. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair per standard building practices.
Substandard repairs were found at one or more locations on the roof surface. Leaks can occur as a result. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend that a qualified contractor evaluate and repair per standard building practices.
44)  Extensions such as splash blocks or drain pipes for one or more downspouts were missing. Water can accumulate around the building foundation or inside crawl spaces or basements as a result. Recommend that a qualified person install, replace or repair extensions as necessary so rainwater drains away from the structure.
Extensions such as splash blocks or drain pipes for one or more downspouts were missing. Water can accumulate around the building foundation or inside crawl spaces or basements as a result. Recommend that a qualified person install, replace or repair extensions as necessary so rainwater drains away from the structure.
45)  Sealant was used at one or more roof penetrations (e.g. pipes, vents, chimneys) rather than flashing. Sealant is not required for most roof penetrations when installations of such items are done professionally and per standard building practices. The presence of sealant suggests that work was performed by someone who was not a qualified contractor. The sealant will be a maintenance issue in the future since it must be renewed periodically. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair where necessary and per standard building practices. For example, by removing sealant and installing flashing.
Sealant was used at one or more roof penetrations (e.g. pipes, vents, chimneys) rather than flashing. Sealant is not required for most roof penetrations when installations of such items are done professionally and per standard building practices. The presence of sealant suggests that work was performed by someone who was not a qualified contractor. The sealant will be a maintenance issue in the future since it must be renewed periodically. Recommend that a qualified contractor repair where necessary and per standard building practices. For example, by removing sealant and installing flashing.
46)  One or more were loose. Rainwater can come in contact with the building exterior or accumulate around the building foundation as a result. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
One or more were loose. Rainwater can come in contact with the building exterior or accumulate around the building foundation as a result. This is a conducive condition for wood-destroying organisms. Recommend that a qualified person repair as necessary.
Attic and Roof Structure
47)  The ceiling insulation installed in the attic was substandard and appeared to have an R rating that's significantly less than current standards (R-38). Heating and cooling costs will likely be higher due to poor energy efficiency. Recommend that a qualified contractor install insulation for better energy efficiency and per standard building practices.
The ceiling insulation installed in the attic was substandard and appeared to have an R rating that's significantly less than current standards (R-38). Heating and cooling costs will likely be higher due to poor energy efficiency. Recommend that a qualified contractor install insulation for better energy efficiency and per standard building practices.
48)  The ceiling insulation in one or more areas of the attic was compacted or uneven. Heating and cooling costs may be higher due to reduced energy efficiency. Recommend that a qualified person repair, replace or install insulation as necessary and per standard building practices (typically R-38).
The ceiling insulation in one or more areas of the attic was compacted or uneven. Heating and cooling costs may be higher due to reduced energy efficiency. Recommend that a qualified person repair, replace or install insulation as necessary and per standard building practices (typically R-38).
Electric
51) 

 Substandard wiring was found at the crawl space. For example, exposed wiring and/or missing or broken cover plates. This is a safety hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and repair as necessary and per standard building practices.
Substandard wiring was found at the crawl space. For example, exposed wiring and/or missing or broken cover plates. This is a safety hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and repair as necessary and per standard building practices.
52) 

 One or more electric receptacles at the kitchen had no visible ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protection, or the inspector was unable to determine if GFCI protection was present. If not GFCI-protected, receptacles in wet areas pose a shock hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and install GFCI protection if necessary and per standard building practices. General guidelines for GFCI-protected receptacles include the following locations:
One or more electric receptacles at the kitchen had no visible ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protection, or the inspector was unable to determine if GFCI protection was present. If not GFCI-protected, receptacles in wet areas pose a shock hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and install GFCI protection if necessary and per standard building practices. General guidelines for GFCI-protected receptacles include the following locations:
https://www.reporthost.com/?GFCI
- Outdoors (since 1973)
- Bathrooms (since 1975)
- Garages (since 1978)
- Kitchens (since 1987)
- Crawl spaces and unfinished basements (since 1990)
- Wet bar sinks (since 1993)
- Laundry and utility sinks (since 2005)
https://www.reporthost.com/?GFCI
53) 

 One or more electric receptacles at the bedroom(s), kitchen, family room and/or laundry area had no visible arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) protection, or the inspector was unable to determine if AFCI protection was present. This is a potential safety hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and install AFCI protection if necessary and per standard building practices. General guidelines for AFCI-protected receptacles include the following locations:
One or more electric receptacles at the bedroom(s), kitchen, family room and/or laundry area had no visible arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) protection, or the inspector was unable to determine if AFCI protection was present. This is a potential safety hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and install AFCI protection if necessary and per standard building practices. General guidelines for AFCI-protected receptacles include the following locations:
https://www.reporthost.com/?AFCI
- Bedrooms (since 1999)
- Kitchens, laundry areas, family rooms, dining rooms, living rooms, parlors, libraries, dens and recreation rooms, sunrooms, closets and hallways (since 2014)
https://www.reporthost.com/?AFCI
54) 

 One or more electric receptacles at the bedroom(s), kitchen, family room and/or laundry area had no visible arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) protection, or the inspector was unable to determine if AFCI protection was present. This is a potential safety hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and install AFCI protection if necessary and per standard building practices. General guidelines for AFCI-protected receptacles include the following locations:
One or more electric receptacles at the bedroom(s), kitchen, family room and/or laundry area had no visible arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) protection, or the inspector was unable to determine if AFCI protection was present. This is a potential safety hazard. Recommend that a qualified electrician evaluate and install AFCI protection if necessary and per standard building practices. General guidelines for AFCI-protected receptacles include the following locations:
https://www.reporthost.com/?AFCI
- Bedrooms (since 1999)
- Kitchens, laundry areas, family rooms, dining rooms, living rooms, parlors, libraries, dens and recreation rooms, sunrooms, closets and hallways (since 2014)
https://www.reporthost.com/?AFCI
55) 
 One or more circuit breakers in panel(s) #A were "double tapped," where two or more wires were installed in the breaker's lug. Most breakers are designed for only one wire to be connected. This is a safety hazard since the lug bolt can tighten securely against one wire but leave other(s) loose. Arcing, sparks and fires can result. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary. For more information, visit:
One or more circuit breakers in panel(s) #A were "double tapped," where two or more wires were installed in the breaker's lug. Most breakers are designed for only one wire to be connected. This is a safety hazard since the lug bolt can tighten securely against one wire but leave other(s) loose. Arcing, sparks and fires can result. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary. For more information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?DBLTAP
https://www.reporthost.com/?DBLTAP
56) 
 Neutral wires were doubled or bundled together under the same lug on the neutral bus bar in panel(s) #. This is a potential safety hazard in the event that one of the circuits needs to be isolated during servicing. For one neutral to be disconnected, other neutrals from energized circuits sharing the same lug will be loosened. Power surges may result on the energized circuits and result in damage or fire. Also, multiple wires under the same lug may not be secure, resulting in loose wires, arcing, sparks and fire. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair per standard building practices. For more information, visit:
Neutral wires were doubled or bundled together under the same lug on the neutral bus bar in panel(s) #. This is a potential safety hazard in the event that one of the circuits needs to be isolated during servicing. For one neutral to be disconnected, other neutrals from energized circuits sharing the same lug will be loosened. Power surges may result on the energized circuits and result in damage or fire. Also, multiple wires under the same lug may not be secure, resulting in loose wires, arcing, sparks and fire. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair per standard building practices. For more information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?DTNB
https://www.reporthost.com/?DTNB
57) 
 One or more modern, 3-slot electric receptacles were found with an open ground. Three-slot receptacles should have a hot, a neutral and a ground wire connected. Homeowners often install new 3-slot receptacles on older, 2-wire circuits that only have hot and neutral wires. This is a shock hazard when appliances that require a ground are used with these receptacles. Examples of such appliances include computers and related hardware, refrigerators, freezers, portable air conditioners, clothes washers, aquarium pumps, and electrically operated gardening tools. Where the electric system was installed prior to when grounded circuits were required (1960s), it is permissible to replace 3-slot receptacles with 2-slot receptacles to prevent appliances that require a ground from being plugged in to an ungrounded circuit. However, the client should be aware of this limitation when planning use for various rooms, such as an office. For newer electric systems, circuits should be repaired so grounded, 3-wire cables provide power to 3-slot receptacles. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair per standard building practices.
One or more modern, 3-slot electric receptacles were found with an open ground. Three-slot receptacles should have a hot, a neutral and a ground wire connected. Homeowners often install new 3-slot receptacles on older, 2-wire circuits that only have hot and neutral wires. This is a shock hazard when appliances that require a ground are used with these receptacles. Examples of such appliances include computers and related hardware, refrigerators, freezers, portable air conditioners, clothes washers, aquarium pumps, and electrically operated gardening tools. Where the electric system was installed prior to when grounded circuits were required (1960s), it is permissible to replace 3-slot receptacles with 2-slot receptacles to prevent appliances that require a ground from being plugged in to an ungrounded circuit. However, the client should be aware of this limitation when planning use for various rooms, such as an office. For newer electric systems, circuits should be repaired so grounded, 3-wire cables provide power to 3-slot receptacles. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair per standard building practices.
58) 
 No permanently installed smoke alarms were found. This is a potential safety hazard. A qualified electrician should install smoke alarms per standard building practices (e.g. in hallways leading to bedrooms, in each bedroom, on each floor and in attached garages). For more information, visit:
No permanently installed smoke alarms were found. This is a potential safety hazard. A qualified electrician should install smoke alarms per standard building practices (e.g. in hallways leading to bedrooms, in each bedroom, on each floor and in attached garages). For more information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?SMKALRM
https://www.reporthost.com/?SMKALRM
59) 
 Smoke alarms were missing from one or more bedrooms, from one or more hallways leading to bedrooms and/or on one or more levels. Smoke alarms should be installed as necessary so a functioning alarm exists in each hallway leading to bedrooms, in each bedroom and on each level. For more information, visit:
Smoke alarms were missing from one or more bedrooms, from one or more hallways leading to bedrooms and/or on one or more levels. Smoke alarms should be installed as necessary so a functioning alarm exists in each hallway leading to bedrooms, in each bedroom and on each level. For more information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?SMKALRM
https://www.reporthost.com/?SMKALRM
60) 
 One or more circuit breakers in panel(s) #A were "double tapped," where two or more wires were installed in the breaker's lug. Most breakers are designed for only one wire to be connected. This is a safety hazard since the lug bolt can tighten securely against one wire but leave other(s) loose. Arcing, sparks and fires can result. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary. For more information, visit:
One or more circuit breakers in panel(s) #A were "double tapped," where two or more wires were installed in the breaker's lug. Most breakers are designed for only one wire to be connected. This is a safety hazard since the lug bolt can tighten securely against one wire but leave other(s) loose. Arcing, sparks and fires can result. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair as necessary. For more information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?DBLTAP
https://www.reporthost.com/?DBLTAP
61) 
 One or more modern, 3-slot electric receptacles were found with an open ground. Three-slot receptacles should have a hot, a neutral and a ground wire connected. Homeowners often install new 3-slot receptacles on older, 2-wire circuits that only have hot and neutral wires. This is a shock hazard when appliances that require a ground are used with these receptacles. Examples of such appliances include computers and related hardware, refrigerators, freezers, portable air conditioners, clothes washers, aquarium pumps, and electrically operated gardening tools. Where the electric system was installed prior to when grounded circuits were required (1960s), it is permissible to replace 3-slot receptacles with 2-slot receptacles to prevent appliances that require a ground from being plugged in to an ungrounded circuit. However, the client should be aware of this limitation when planning use for various rooms, such as an office. For newer electric systems, circuits should be repaired so grounded, 3-wire cables provide power to 3-slot receptacles. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair per standard building practices.
One or more modern, 3-slot electric receptacles were found with an open ground. Three-slot receptacles should have a hot, a neutral and a ground wire connected. Homeowners often install new 3-slot receptacles on older, 2-wire circuits that only have hot and neutral wires. This is a shock hazard when appliances that require a ground are used with these receptacles. Examples of such appliances include computers and related hardware, refrigerators, freezers, portable air conditioners, clothes washers, aquarium pumps, and electrically operated gardening tools. Where the electric system was installed prior to when grounded circuits were required (1960s), it is permissible to replace 3-slot receptacles with 2-slot receptacles to prevent appliances that require a ground from being plugged in to an ungrounded circuit. However, the client should be aware of this limitation when planning use for various rooms, such as an office. For newer electric systems, circuits should be repaired so grounded, 3-wire cables provide power to 3-slot receptacles. Recommend that a qualified electrician repair per standard building practices.
62) 
 One or more knockouts were missing from panel(s) #A. Holes in panels are a potential fire hazard if a malfunction ever occurs inside the panel. Rodents can also enter panels through holes. Recommend that a qualified person install knockout covers where missing and per standard building practices.
One or more knockouts were missing from panel(s) #A. Holes in panels are a potential fire hazard if a malfunction ever occurs inside the panel. Rodents can also enter panels through holes. Recommend that a qualified person install knockout covers where missing and per standard building practices.
63) 
 No permanently installed carbon monoxide alarms were found. This is a potential safety hazard. Some states and/or municipalities require CO alarms to be installed for new construction and/or for homes being sold. Recommend installing approved CO alarms outside of each separate sleeping area in the immediate vicinity of the bedrooms on each level and in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. For more information, visit:
No permanently installed carbon monoxide alarms were found. This is a potential safety hazard. Some states and/or municipalities require CO alarms to be installed for new construction and/or for homes being sold. Recommend installing approved CO alarms outside of each separate sleeping area in the immediate vicinity of the bedrooms on each level and in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. For more information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?COALRM
https://www.reporthost.com/?COALRM
64) 
 Carbon monoxide alarms were missing from one or more sleeping areas and/or on one or more levels. This is a potential safety hazard. Some states and/or municipalities require CO alarms to be installed in the vicinity of each sleeping area, on each level and in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. Recommend installing additional carbon monoxide alarms per these standards. For more information, visit:
Carbon monoxide alarms were missing from one or more sleeping areas and/or on one or more levels. This is a potential safety hazard. Some states and/or municipalities require CO alarms to be installed in the vicinity of each sleeping area, on each level and in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. Recommend installing additional carbon monoxide alarms per these standards. For more information, visit:
https://www.reporthost.com/?COALRM
https://www.reporthost.com/?COALRM
65) 
 One or more screws used to secure the cover or dead front to panel(s) #A had sharply pointed tips or were too long. Energized wires can be damaged by such screws. This is a potential shock hazard, especially when screws are being removed or installed. Recommend that a qualified person replace such screws with screws that are approved for this purpose (e.g. blunt-tip screws of the correct length). Because energized wires may be in contact with these screws, the client should consider having a qualified electrician replace the screws.
One or more screws used to secure the cover or dead front to panel(s) #A had sharply pointed tips or were too long. Energized wires can be damaged by such screws. This is a potential shock hazard, especially when screws are being removed or installed. Recommend that a qualified person replace such screws with screws that are approved for this purpose (e.g. blunt-tip screws of the correct length). Because energized wires may be in contact with these screws, the client should consider having a qualified electrician replace the screws.
66) 
 Branch circuit wiring installed in buildings built prior to the mid 1980s is typically rated for a maximum temperature of only 60 degrees Celsius. This includes non-metallic sheathed (Romex) wiring, and both BX and AC metal-clad flexible wiring. Knob and tube wiring, typically installed in homes built prior to 1950, may be rated for even lower maximum temperatures. Newer electric fixtures including lighting and fans typically require wiring rated for 90 degrees Celsius. Connecting newer fixtures to older, 60-degree-rated wiring is a potential fire hazard. Repairs for such conditions may involve replacing the last few feet of wiring to newer fixtures with new 90-degree-rated wire, and installing a junction box to join the old and new wiring.
Branch circuit wiring installed in buildings built prior to the mid 1980s is typically rated for a maximum temperature of only 60 degrees Celsius. This includes non-metallic sheathed (Romex) wiring, and both BX and AC metal-clad flexible wiring. Knob and tube wiring, typically installed in homes built prior to 1950, may be rated for even lower maximum temperatures. Newer electric fixtures including lighting and fans typically require wiring rated for 90 degrees Celsius. Connecting newer fixtures to older, 60-degree-rated wiring is a potential fire hazard. Repairs for such conditions may involve replacing the last few feet of wiring to newer fixtures with new 90-degree-rated wire, and installing a junction box to join the old and new wiring.
It is beyond the scope of this inspection to determine if such incompatible components are installed, or to determine the extent to which they're installed. Based on the age of this building, the client should be aware of this safety hazard, both for existing fixtures and when planning to upgrade with newer fixtures. Consult with a qualified electrician for repairs as necessary.
It is beyond the scope of this inspection to determine if such incompatible components are installed, or to determine the extent to which they're installed. Based on the age of this building, the client should be aware of this safety hazard, both for existing fixtures and when planning to upgrade with newer fixtures. Consult with a qualified electrician for repairs as necessary.
67) 
 The legend for circuit breakers or fuses in panel(s) #A was missing, incomplete, illegible or confusing. This is a potential shock or fire hazard in the event of an emergency when power needs to be turned off. Recommend correcting the legend so it's accurate, complete and legible. Evaluation by a qualified electrician may be necessary.
The legend for circuit breakers or fuses in panel(s) #A was missing, incomplete, illegible or confusing. This is a potential shock or fire hazard in the event of an emergency when power needs to be turned off. Recommend correcting the legend so it's accurate, complete and legible. Evaluation by a qualified electrician may be necessary.
